Translate this page into:
Calcific Periarthritis of Metacarpophalangeal Joint Secondary to Ruptured Calcific Dorsal Bursitis – A Case Report

*Corresponding author: D. Sunil Kumar, Department of Radiodiagnosis, Jawaharlal Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education and Research, Gorimedu, Pondicherry - 605 006, India. sunil.chendur@gmail.com
-
Received: ,
Accepted: ,
How to cite this article: Niveditha KH, Kumar GR, Kumar DS, Kashyap R. Calcific Periarthritis of Metacarpophalangeal Joint Secondary to Ruptured Calcific Dorsal Bursitis – A Case Report. Indian J Musculoskelet Radiol 2020;2(2):152-5.
Abstract
Acute calcific periarthritis (ACP) is a painful monoarticular disease commonly involving the shoulder joint, characterized by deposits of calcium hydroxyapatite crystals around joints. Clinical mimics include septic arthritis, gout, and pseudogout. It is a rare disease of hand and only few cases have been reported. We describe the imaging findings of ACP of metacarpophalangeal joint secondary to ruptured calcific dorsal bursitis, in a 30-year-old woman who presented with complaints of local pain and swelling of the left fourth finger. Accurate diagnosis of this condition is essential to avoid unnecessary investigations, procedures, and patient anxiety.
Keywords
Calcific periarthritis
Dorsal bursitis
Calcific bursitis
Magnetic resonance imaging
Ultrasonography
Radiograph
INTRODUCTION
Acute calcific periarthritis (ACP) is a rare cause of severe acute periarticular inflammatory process in the hand with juxta-articular calcium hydroxyapatite deposition.[1] Calcific bursitis occurs due to inflammation secondary to crystal deposition in periarticular bursa and it can be associated with calcific tendinitis. This condition is frequently seen around shoulder joint with rare involvement of other joints. Underdiagnosis of this condition is not uncommon due to unusual site of involvement like hand. In this report, we describe in detail the imaging findings in a case of ACP involving metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joint secondary to ruptured calcific dorsal bursitis.
CASE REPORT
A 30-year-old, right-handed female, typist by occupation came to the OPD with a 2 weeks history of severe progressive left hand pain and swelling localized to dorsum of the metacarpal head of fourth finger. She gave no history of trauma, fever, or insect bite to that region or other joint involvement. On palpation, there were tenderness and soft-tissue swelling in the MCP joint of fourth finger. Laboratory analysis disclosed normal white blood cells count, normal uric acid levels, and no other significant abnormality. Radiographs, local ultrasound, and MR imaging were performed with a clinical concern of infective etiology.
Radiograph of the left hand showed well-circumscribed lobulated cloudy calcific mass along the radial aspect of MCP joint of the fourth finger with preserved periarticular bone density [Figure 1a]. The joint space appeared normal with no bony erosion.
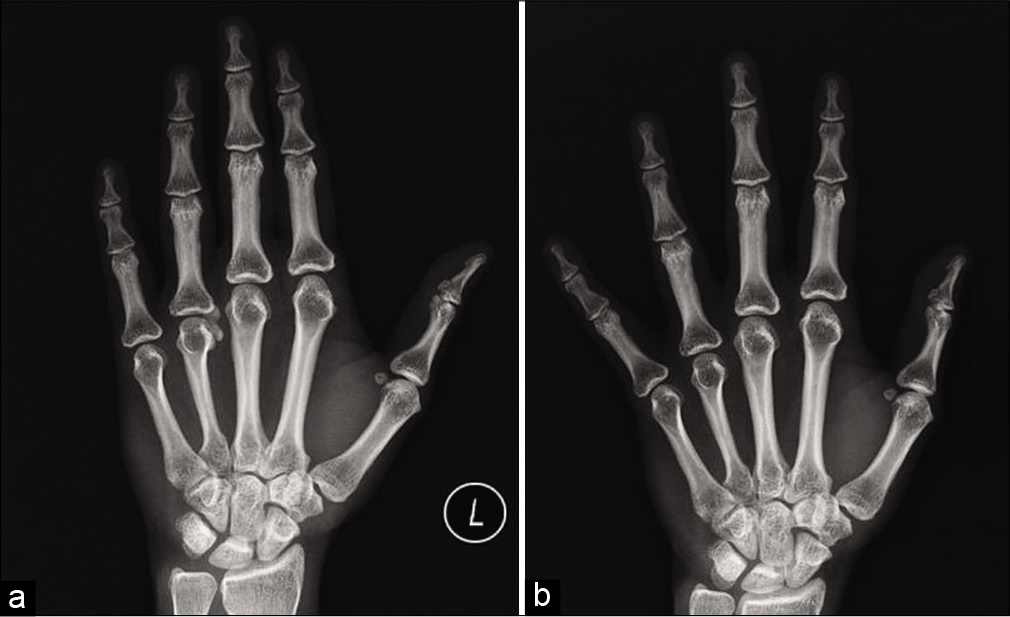
- (a) Radiograph PA view of the left hand shows a well-defined cloudy calcification with lobulated margins along the radial aspect of the 4th metacarpophalangeal joint. (b) Radiograph PA view of the left hand after 7 weeks of conservative management showing complete resolution of cloudy calcification.
Local ultrasound was performed using Siemens ACUSON S3000 with a high-frequency linear probe 18 L6HD (bandwidth 5.5–18.0 MHz, 57 mm footprint). It revealed partially collapsed fluid-filled dorsal bursa with thickened hypertrophied wall [Figure 2a-d]. The radial side of the bursa was poorly delineated with an ill-defined heterogeneous lesion with echogenic areas within, in the periarticular location in the radial aspect of fourth metacarpal bone, corresponding to the cloudy calcific opacity in the radiograph. Extensor tendon appeared normal. No joint space involvement or joint space effusion noted. Ultrasound findings were suggestive of ruptured calcific bursitis.
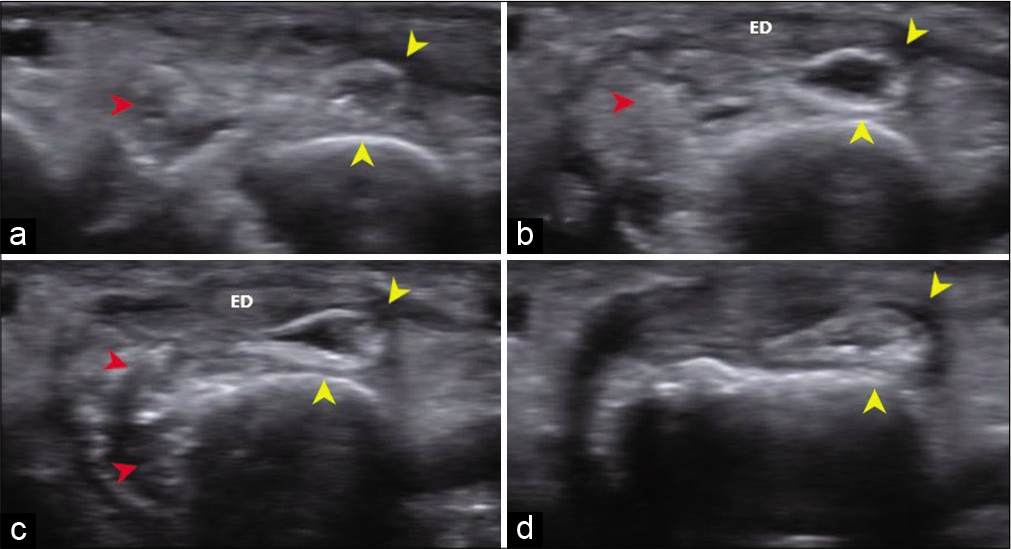
- (a-d) Local USG – axial sections from proximal to distal, shows a partially collapsed fluid-filled dorsal bursa with thickened wall (yellow arrow heads). Radial aspect of the bursal wall is poorly delineated. An ill-defined heterogeneous lesion with echogenic areas within corresponding to the calcific inflammatory infiltrate (red arrow heads) is noted in the periarticular location along the radial aspect of the fourth metacarpal bone. Extensor digitorum (ED) tendon appeared normal.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) was performed using a Siemens Skyra 3 Tesla Scanner with dedicated wrist coils. MRI showed an ill-defined lesion, isointense on T1-weighted images, and hyperintense on T2-weighted and proton density fat-suppressed images; in the periarticular location along the radial aspect and dorsum of the fourth metacarpophalangeal joint, deep to the extensor digitorum tendon corresponding to the site of calcification seen on the radiograph [Figures 3a and b, 4]. The partially collapsed, fluid-filled dorsal bursa was seen in T2 and PDFS images. Few T2/PDFS hypointense areas were seen representing calcifications. No evidence of ossification was noted. The extensor digitorum tendon appeared normal. Post-contrast [Figure 5] images showed the peripherally enhancing fluid-filled hypertrophied dorsal bursa deep to extensor tendon of the fourth MCP joint with non-uniform enhancement of the inflammatory infiltrate in radial aspect of MCP joint and head of metacarpal bone. The radial side of the bursa appeared collapsed compared to the ulnar side. Mild marrow edema was noted in the radial aspect of metacarpal head with mild enhancement in post-contrast images.
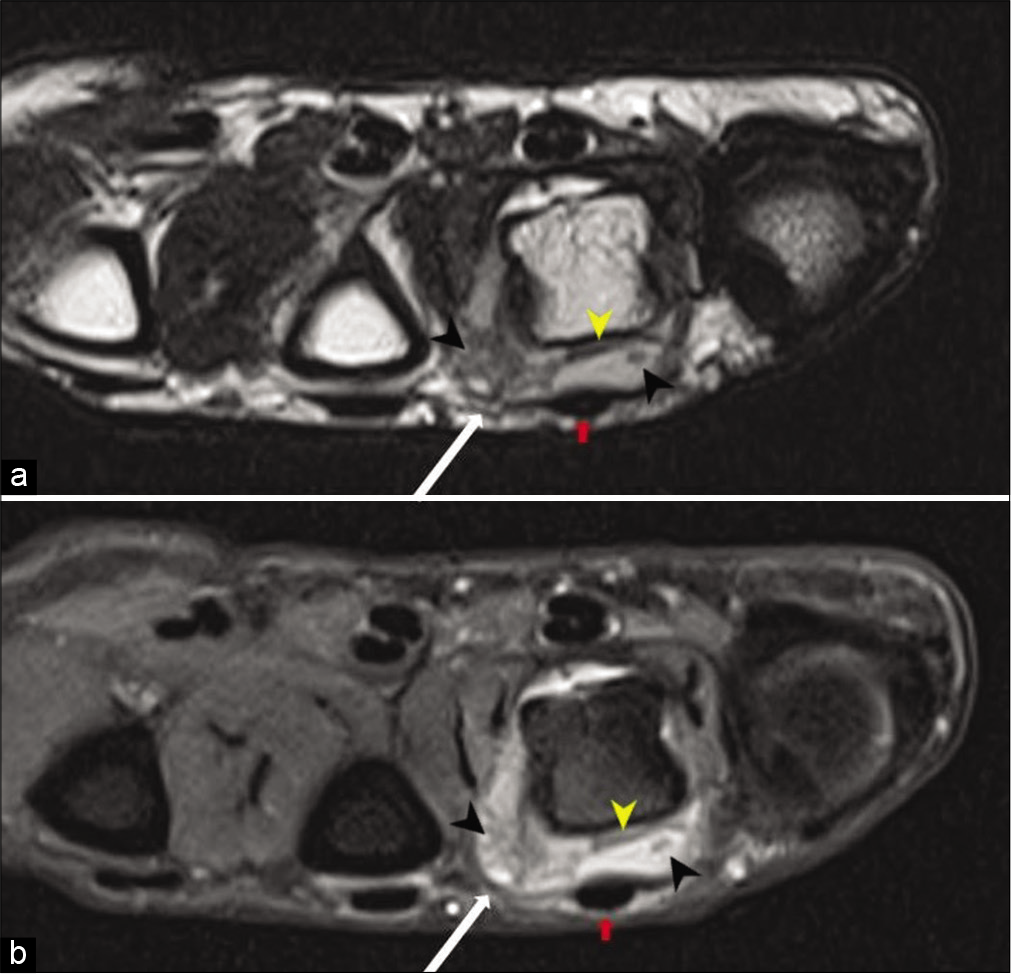
- Axial T2 (a) and PDFS (b) images show a fluid-filled hypertrophied dorsal bursa (yellow arrow heads) deep to the extensor digitorum tendon (red arrows). A well-defined heterogeneous hyperintense lesion (white arrows) is seen in the dorsal and radial aspect of the 4th metacarpophalangeal joint. Areas of T2/PDFS hypointensity (black arrow heads) are seen within the bursa and periarticular region corresponding to calcification. Mild PDFS hyperintensity representing marrow edema is seen in the radial aspect of the metacarpal head.
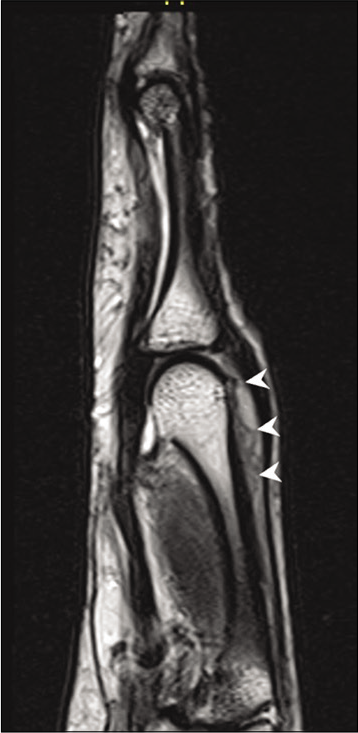
- Sag T2 image shows the inflammatory infiltrate as a hyperintense lesion (arrow heads) deep to the extensor digitorum tendon. No involvement of joint space is seen.
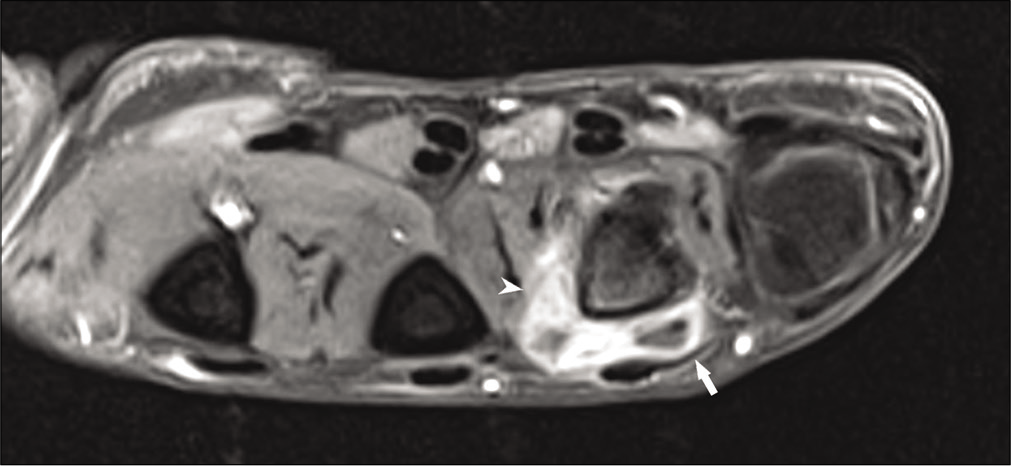
- Post-contrast T1 FS images show peripherally enhancing bursa (white arrow) with non-uniform enhancement of the inflammatory infiltrate (arrow head). Mild post-contrast enhancement of the marrow is seen in the radial aspect of the metacarpal head.
The diagnosis of ACP secondary to ruptured calcific bursitis was made. This diagnosis was made based on the clinical and radiological characteristics.
The patient was managed conservatively with NSAIDs and hot fomentation. She had significant relief of symptoms within 2 weeks, follow-up radiograph after 7 weeks showed complete resolution of the amorphous calcifications [Figure 1b].
DISCUSSION
ACP is a self-limiting inflammatory condition that manifests as severe pain, edema, and redness localized to a single joint and is characterized by periarticular calcifications in radiograph. Typically, ACP is monoarticular and is commonly noted in the proximal joints – the shoulder joint followed by the hip joint.[2] Involvement of the hand is uncommon. The most common site involved in hand is the flexor carpi ulnaris tendon at its insertion site, and in fingers, it is the MCP joint.[3] It commonly affects the women of perimenopausal age with average age of presentation being 35 years.[4]
The etiology of ACP is not clearly understood. This condition may be related to the degenerative process affecting tendon, bursa, or joint capsule secondary to local hypoxia or microtrauma with subsequent necrosis, leading to deposition of calcium crystals. Patients are usually symptom free during the early phase and acute pain results from the rupture of crystal deposits into the surrounding soft tissues that trigger an acute inflammatory process causing localized pain, swelling, and redness.[5] This process resolves spontaneously by phagocytosis restoring the normal structure of tendon and joint capsule. Association of ACP includes few autoimmune conditions such as hypothyroidism, systemic sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, and other metabolic conditions such as diabetes, gout, and pseudogout.[6]
Radiographic findings may help in differentiating ACP and pyogenic arthritis. Calcifications are not usually seen in pyogenic arthritis. Although they can occur months to years later, if the infection is inadequately treated. However, in ACP, calcifications can be seen even before the onset of clinical symptoms.
Radiographically, a number of conditions present with periarticular calcifications. Typically, the calcifications in ACP are seen as homogenous, amorphous densities with either well-defined or ill-defined margins. They do not demonstrate cortex or internal trabeculations.[2] There may be temporal change in morphology of calcifications, and they gradually show complete resolution.[7]
Sometimes, the calcifications can mimic a cortical avulsion fracture. An avulsion fracture shows a defect in the parent bone.
As ACP is characteristically a monoarticular condition with maintained joint space, it can be differentiated from other inflammatory arthritis such as rheumatoid, psoriatic arthritis, and systemic sclerosis, which are usually polyarticular with reduced or widened joint space and periarticular erosions. Heterotopic ossification and accessory ossicles demonstrate cortex and internal trabeculations.
Crystal-induced arthritis such as gout and calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate (CPPD) can be considered for periarticular soft-tissue calcifications. However, the absence of periarticular erosions and soft-tissue mass renders gouty arthritis unlikely. CPPD arthropathy of hand, although rare, can present with acute attacks and periarticular calcification mimicking ACP, but it is generally associated with articular cartilage calcification and degenerative changes in the joints.
Calcifications in tumoral calcinosis are large and globular and it is usually associated with renal dysfunction. Other rare periarticular soft-tissue tumors like synovial sarcomas are often partially mineralized with soft-tissue mass with punctate and peripheral calcifications.
In MRI, calcifications generally appear hypointense on T2-weighted images. However, in calcific periarthritis, the T2 shortening effect of calcifications can be masked by the surrounding inflammatory infiltrate which has longer T2 relaxation time.[5] Hence, these lesions may appear hyperintense on T2-weighted images. In our patient, the lesion was predominantly hyperintense secondary to the inflammatory infiltrate and there were areas of hypointensity within the inflammatory infiltrate which may represent the calcium deposits.
The extensor digitorum tendon is stabilized at the MCP joint on either side by triangular aponeuroses referred to as dorsal extensor expansion.[8] It holds the extensor tendon in central position and prevents it from subluxation. It slides distally and proximally when the finger is flexed and extended, respectively. This movement of extensor tendon and dorsal extensor expansion over the MCP is facilitated by two lateral bursae and a dorsal bursa [Figure 6]. The dorsal bursa separates the dorsal aspect of the MCP joint from the extensor digitorum tendon apparatus.[9] Our patient was a typist – an occupation which involves overuse of the MCP joint and the extensor apparatus. This might have subjected the dorsal bursa to increased pressures, leading to inflammation.
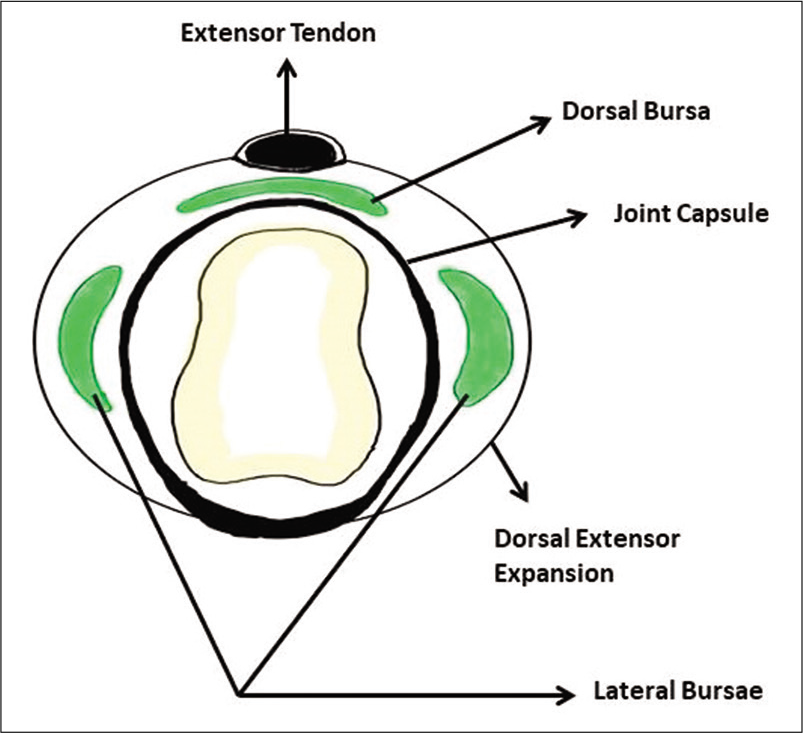
- Schematic diagram – axial section at the level of metacarpal head.
ACP is a self-limiting joint disease. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs with immobilization of involved joint can be advised for symptomatic relief. Earlier this condition was treated with surgical evacuation and radiation,[3] but they are obsolete now. Invasive treatment options such as US-guided injection of steroids or local anesthetics and aspiration of crystal deposits are reserved for severe cases which are not responding to conservative management for several months.[10] The calcifications seen on radiographs usually disappear over the course of weeks without any medical or surgical intervention.[3,10]
CONCLUSION
Diagnostic error of calcific periarthritis of hand is not uncommon due to its unusual occurrence and its clinical mimic of infectious and other inflammatory entities. Homogeneous and amorphous calcifications with no internal characteristics and no periarticular erosions should raise the possibility of ACP in the diagnosis of acute arthritis of the hand joints. Good clinicoradiological correlation helps to avoid unnecessary expensive diagnostic tests, invasive procedures, and inappropriate medication.
Declaration of patient consent
The authors certify that they have obtained all appropriate patient consent.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
References
- Diagnostic dilemma: Acute calcific tendinitis of flexor digitorum profundus. Hand (N Y). 2013;8:352-3.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calcium hydroxyapatite deposition disease. Radiographics. 1990;10:1031-48.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peritendinitis calcarea: A common disease of middle life: Its diagnosis, pathology, and treatment. J Roentgenol. 1938;40:1-21.
- [Google Scholar]
- Acute calcium deposits in the hand and wrist; comparison of acute calcium peritendinitis and acute calcium periarthritis. J Hand Surg. 2014;39:436-9.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AJR teaching file: Periarticular calcifications in two patients with acute hand pain. Am J Roentgenol. 2010;195:76-9.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Acute calcific periarthritis of proximal interphalangeal joints in a professional golfer's hand. J Korean Med Sci. 2004;19:904-6.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Acute calcific periarthritis of the hand and wrist: A series and review of the literature. Emerg Radiol. 2007;14:199-203.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrist and hand In: Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier; 2008. p. :880-1.
- [Google Scholar]
- The anatomy of the metacarpo-phalangeal joints, with observations of the aetiology of ulnar drift. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1975;57:485-90.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Acute calcific periarthritis of the hand and elbows in women: A study and review of the literature. J Rheumatol. 1993;20:1533-8.
- [Google Scholar]






